-
 FAST SHIPPING
FAST SHIPPING
-
 COMPETITIVE PRICE
COMPETITIVE PRICE
-
 EXCELLENT AFTER-SERVICE
EXCELLENT AFTER-SERVICE
- Home
- Products
- PV Panel
- Full Black Solar PV Modules TP 410W
- Full Black Bifacial Solar PV Modules 420W
- Full Black Solar PV Modules TP 430W
- Solar Module 550W
- Flexible Solar Module 375W
- LONGi-LR5-72HTH-565W Silver Frame Solar Panel
- SUNTECH-STP420S-420W Full Black Solar Panel
- JASolar 435W JAM54D41 Full Black Bifacial Glass Solar Panel
- TW SOLAR 610W MNH66HD Bifacial Solar Panel
- Jinko 620W 66HL4M-BDV Bifacial Solar Panel
- Solar Inverter
- Solar Storage Battery
- Residential Photovoltaic Kits
- Solar Panel Brackets
- Balcony/Garden Photovoltaic Kits
- Outdoor Power Station
- Deye SUN-8K-SG04LP3-EU Three Phase Low Voltage Hybrid Inverter
- Photovoltaic Accessory
- C&I ESS Solution
- PV Panel
- About Us
- News & Events
- Contact Us
Web Menu
- Home
- Products
- PV Panel
- Full Black Solar PV Modules TP 410W
- Full Black Bifacial Solar PV Modules 420W
- Full Black Solar PV Modules TP 430W
- Solar Module 550W
- Flexible Solar Module 375W
- LONGi-LR5-72HTH-565W Silver Frame Solar Panel
- SUNTECH-STP420S-420W Full Black Solar Panel
- JASolar 435W JAM54D41 Full Black Bifacial Glass Solar Panel
- TW SOLAR 610W MNH66HD Bifacial Solar Panel
- Jinko 620W 66HL4M-BDV Bifacial Solar Panel
- Solar Inverter
- Solar Storage Battery
- Residential Photovoltaic Kits
- Solar Panel Brackets
- Balcony/Garden Photovoltaic Kits
- Outdoor Power Station
- Deye SUN-8K-SG04LP3-EU Three Phase Low Voltage Hybrid Inverter
- Photovoltaic Accessory
- C&I ESS Solution
- PV Panel
- About Us
- News & Events
- Contact Us
Product Search
Exit Menu
Product categories
News categories
RECENT POSTS
-
Why Thermal Management Is the Unsung Hero of High-Power EV Charging Pile Performance
Apr 28,2025 -
How Power Electronics Are Shaping the Performance and Efficiency of Modern EV Charging Piles
Apr 23,2025 -
Lietuva investuoja į tvarumą: 15 mln. eurų parama atokiems saulės energijos parkams plėtoti
Apr 21,2025 -
Lithuanian Government Introduces €15 Million Scheme to Support the Development of Remote Solar Power Plants
Apr 21,2025 -
Atnaujintos paramos sąlygos saulės elektrinėms: virš 50 mln. Eur kvietimai jau vasario pabaigoje
Apr 21,2025
AC vs. DC Charging: Unraveling the Electric Vehicle Dilemma
As electric vehicles (EVs) continue to surge in popularity, understanding the intricacies of how they charge becomes increasingly vital for both current and prospective owners. One of the most critical aspects of EV charging lies in the distinction between alternating current (AC) and direct current (DC) charging. While both types of current are essential for charging electric vehicles, they operate differently, leading to significant variations in charging time and efficiency.
To begin with, it's important to note that electric vehicle batteries can only store direct current (DC), whereas the electricity supplied from the grid is always in alternating current (AC). This fundamental difference is key to understanding the nuances of EV charging. When you plug your vehicle into an AC EV Charging Pile, the electricity flows into the vehicle's onboard charger, which then converts the AC power into DC to store in the battery. This process inherently adds a layer of complexity and can slow down the charging process, as the speed of charging is limited by the capacity of that onboard charger. Typically, home EV chargers and many public charging stations utilize AC charging, providing a convenient option for daily use. However, the charging rates can vary significantly, with standard home chargers usually offering power outputs between 3.7 kW and 22 kW. This means that, while you might fully recharge your vehicle overnight, it may not be the fastest solution for those in need of a quick top-up.
On the other hand, DC charging revolutionizes the way we think about charging time. In this scenario, the conversion from AC to DC occurs within the charging station itself, allowing the electricity to be sent directly to the vehicle’s battery. This process eliminates the need for an onboard charger to handle the conversion, resulting in significantly faster charging times. DC chargers, often found in public stations designed for rapid and ultra-rapid charging, can deliver anywhere from 50 kW to over 350 kW of power, enabling drivers to recharge their vehicles to about 80% in as little as 30 minutes. This is particularly advantageous for long-distance travel, where quick stops at charging stations can minimize downtime.
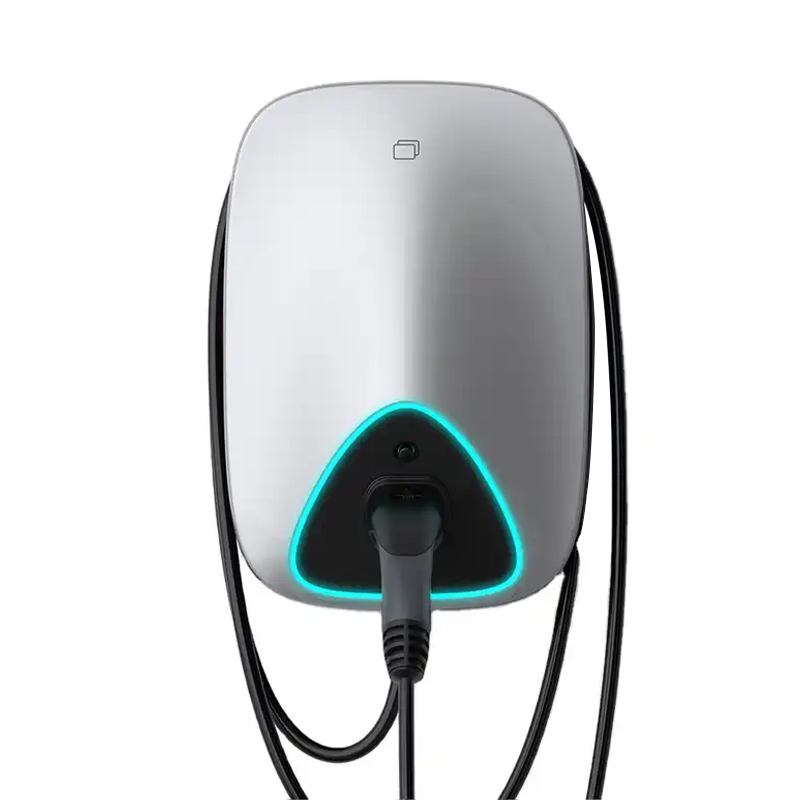

However, while DC charging offers speed and convenience, it does come with some considerations. Frequent use of DC fast charging can lead to increased heat generation, which may affect battery longevity over time. Manufacturers often advise using DC charging primarily for long journeys and opting for AC charging in daily routines. Balancing the two types of charging allows for optimal battery health and performance while providing the flexibility to recharge in various scenarios.
The choice between AC and DC charging boils down to individual needs and usage patterns. For those who drive primarily in urban environments and can charge at home, an AC charger may be sufficient and more economical. In contrast, long-distance travelers or fleet operators may find that investing in access to DC charging infrastructure pays off in the form of time savings and convenience. As the EV market continues to evolve, understanding these differences in charging technology will be crucial for making informed decisions about vehicle use, charging options, and the overall impact on battery life and efficiency.
In a world where electric vehicles are becoming a common sight on the roads, grasping the nuances of charging methods not only enhances your ownership experience but also contributes to the broader transition toward sustainable transportation. Whether you're planning your daily commute or mapping out a road trip, knowing how AC and DC charging can impact your journey will ensure you're always prepared to hit the road with confidence.
←
Ukraine's Energy Struggle: Zelensky States That Almost All Thermal and Hydroelectric Power Generation Capacity Has Been Lost
→
What is the best orientation for solar panels to maximize sunlight exposure?
related products
 +39 3444606026
+39 3444606026 [email protected]
[email protected] De Werf 11, 2544 EH The Hague, The Nederland.
De Werf 11, 2544 EH The Hague, The Nederland. WhatsApp: +1 (917) 257 2995
WhatsApp: +1 (917) 257 2995
Copyright © 2023 Uni Z International B.V. VAT: NL864303440B01 All Rights Reserved



 0
0


 italiano
italiano Polskie
Polskie Nederlands
Nederlands Deutsch
Deutsch Français
Français Español
Español Український
Український