-
 FAST SHIPPING
FAST SHIPPING
-
 COMPETITIVE PRICE
COMPETITIVE PRICE
-
 EXCELLENT AFTER-SERVICE
EXCELLENT AFTER-SERVICE
- Home
- Products
- PV Panel
- Full Black Solar PV Modules TP 410W
- Full Black Bifacial Solar PV Modules 420W
- Full Black Solar PV Modules TP 430W
- Solar Module 550W
- Flexible Solar Module 375W
- LONGi-LR5-72HTH-565W Silver Frame Solar Panel
- SUNTECH-STP420S-420W Full Black Solar Panel
- JASolar 435W JAM54D41 Full Black Bifacial Glass Solar Panel
- TW SOLAR 610W MNH66HD Bifacial Solar Panel
- Jinko 620W 66HL4M-BDV Bifacial Solar Panel
- Solar Inverter
- Solar Storage Battery
- Residential Photovoltaic Kits
- Solar Panel Brackets
- Balcony/Garden Photovoltaic Kits
- Outdoor Power Station
- EV charging pile
- Photovoltaic Accessory
- C&I ESS Solution
- PV Panel
- About Us
- News & Events
- Contact Us
Web Menu
- Home
- Products
- PV Panel
- Full Black Solar PV Modules TP 410W
- Full Black Bifacial Solar PV Modules 420W
- Full Black Solar PV Modules TP 430W
- Solar Module 550W
- Flexible Solar Module 375W
- LONGi-LR5-72HTH-565W Silver Frame Solar Panel
- SUNTECH-STP420S-420W Full Black Solar Panel
- JASolar 435W JAM54D41 Full Black Bifacial Glass Solar Panel
- TW SOLAR 610W MNH66HD Bifacial Solar Panel
- Jinko 620W 66HL4M-BDV Bifacial Solar Panel
- Solar Inverter
- Solar Storage Battery
- Residential Photovoltaic Kits
- Solar Panel Brackets
- Balcony/Garden Photovoltaic Kits
- Outdoor Power Station
- EV charging pile
- Photovoltaic Accessory
- C&I ESS Solution
- PV Panel
- About Us
- News & Events
- Contact Us
Product Search
Exit Menu
Product categories
News categories
RECENT POSTS
-
Why MPPT and PWM Controllers Matter in Folding Solar Panel Systems for Reliable Performance
Apr 15,2025 -
Maximizing Efficiency with Residential Photovoltaic Kits: Optimizing Energy Storage and Management for Your Home
Apr 07,2025 -
Maximize Safety and Stability with the Balcony Triangle Bracket: Essential Features Explained
Apr 01,2025 -
How to Choose the Best Folding Solar Panel for Your Outdoor Adventures
Mar 24,2025 -
Maximizing Solar Power: Choosing the Right Solar Storage Battery
Mar 18,2025
Structural and Mechanical Engineering Insights on Solar Panel Brackets
To installing solar panels, choosing the right solar panel brackets isn’t just about securing them in place—it’s about ensuring long-term performance, efficiency, and structural safety. A well-designed mounting system must withstand environmental forces, distribute weight effectively, and maintain optimal panel positioning to maximize energy generation. Understanding the structural and mechanical engineering principles behind these brackets is crucial for both installers and system owners.
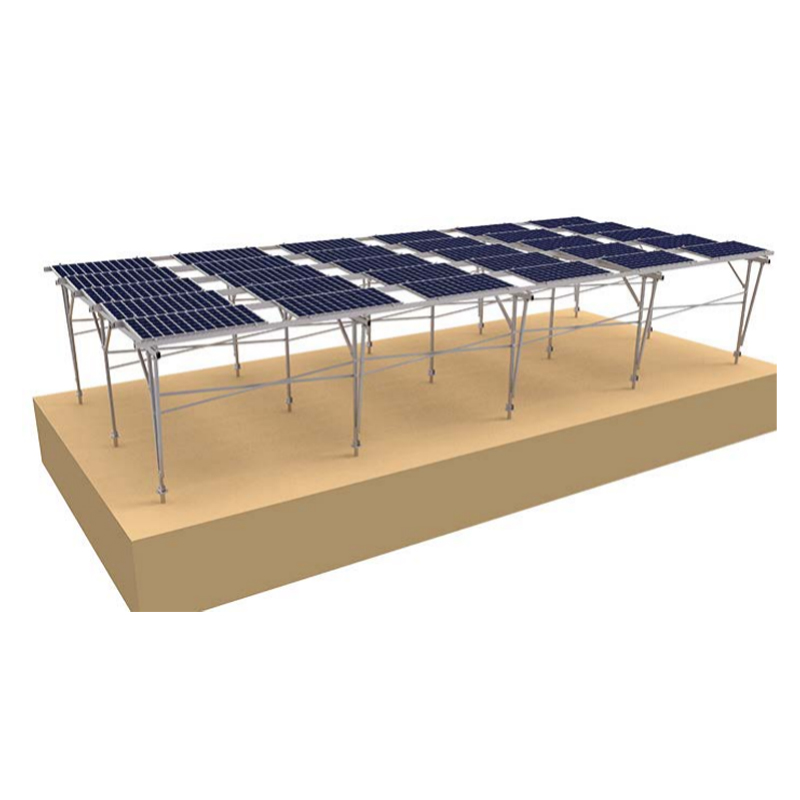

One of the key factors in designing durable mounting brackets is load resistance. Solar panel systems are constantly exposed to wind, snow, and seismic forces, which can create significant stress on the mounting structure. Wind load, for instance, exerts both uplift and lateral forces on solar panels, and if the brackets are not engineered correctly, panels can become loose or even detach. This is why engineers conduct wind tunnel testing and computational simulations to determine the ideal bracket strength for various climate conditions. Similarly, in snowy regions, brackets must be able to handle the extra weight from accumulated snow, ensuring the system remains stable and functional through harsh winters. Seismic loads are another critical consideration, especially in earthquake-prone areas. Flexible yet strong bracket designs help absorb shocks and prevent damage during seismic activity, reducing the risk of structural failure.
Beyond external forces, material selection plays a fundamental role in the performance of solar panel mounting brackets. Aluminum and stainless steel are commonly used due to their corrosion resistance and strength-to-weight ratio. Aluminum brackets are lightweight and naturally resistant to rust, making them ideal for rooftop installations where reducing roof load is a priority. Stainless steel, on the other hand, offers superior tensile strength, making it a preferred choice for ground-mounted and high-wind applications. Engineers must also consider factors such as thermal expansion and contraction, ensuring that the materials used in brackets can withstand temperature fluctuations without warping or weakening over time.
Another aspect of bracket engineering is stress distribution and durability testing. Poorly designed brackets can create uneven weight distribution, leading to stress concentration points that weaken over time. To prevent this, manufacturers use finite element analysis (FEA) software to simulate real-world conditions and optimize bracket geometry. Testing protocols such as cyclic load testing help assess long-term durability, ensuring the brackets can endure repeated environmental stress without failure.
Lastly, advancements in mounting technology have introduced new solutions such as tracker-compatible brackets. Unlike fixed-tilt systems, solar tracking systems require brackets with additional mechanical complexity to allow movement and adjust panel angles throughout the day. These innovations help maximize solar energy capture but also introduce new engineering challenges, such as increased wear and tear on moving parts. As the industry continues to evolve, the demand for more adaptable and resilient solar panel brackets will drive further advancements in bracket design, making solar installations more efficient and reliable than ever.
←
Balancing Power and Sustainability: EV Charging Pile’s Role in Smart Grids
→
Maximizing Solar Storage Battery Efficiency: Smart Energy Management Tips
related products
 +39 3444606026
+39 3444606026 [email protected]
[email protected] De Werf 11, 2544 EH The Hague, The Nederland.
De Werf 11, 2544 EH The Hague, The Nederland.
Copyright © 2023 Uni Z International B.V. VAT: NL864303440B01 All Rights Reserved



 0
0


 italiano
italiano Polskie
Polskie Nederlands
Nederlands Deutsch
Deutsch Français
Français Español
Español Український
Український